This flashcard is just one of a free flashcard set. See all flashcards!
9
Prove why creating a Delaunay Triangulation using edge flipping terminates using Seidel's Parabolic Map!
Lift every vertex onto a parabola:
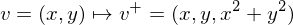
A circle in the plane maps to an ellipsoid on the parabola. This ellipsoid lies in a plane. Every point on the ground which lies inside the circle lifts to a point below the plane. Every point on the ground which lies outside the circle lifts to a point above the plane.
Suppose have a non-Delaunay pair of triangles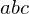 ,
,  in the plane, where
in the plane, where 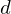 lies in
lies in 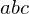 's circumcircle.
's circumcircle.
The lifted points lie in the same plane as the lifted ellipse of
lie in the same plane as the lifted ellipse of 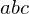 's circumcircle. Since
's circumcircle. Since 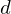 lies inside the circle,
lies inside the circle, lies below the plane of
lies below the plane of 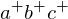 . Thus, the edge
. Thus, the edge  is reflex.
is reflex.
By flipping the edge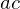 to
to 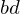 , we replace the reflex edge
, we replace the reflex edge  by the convex edge
by the convex edge  .
.
Note that the four points form a tetrahedron. Before the flip, our triangulation corresponded to the upward-facing faces of the tetrahedron. After the flip, it corresponded to the downward-facing faces of the tetrahedron.
form a tetrahedron. Before the flip, our triangulation corresponded to the upward-facing faces of the tetrahedron. After the flip, it corresponded to the downward-facing faces of the tetrahedron.
Thus, with each flip, we monotonically decrease the height of our triangulation on the paraboloid. Tetrahedral edges which lie on the upward-facing side are never considered again. Thus, the algorithm terminates eventually.
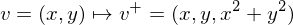
A circle in the plane maps to an ellipsoid on the parabola. This ellipsoid lies in a plane. Every point on the ground which lies inside the circle lifts to a point below the plane. Every point on the ground which lies outside the circle lifts to a point above the plane.
Suppose have a non-Delaunay pair of triangles
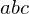 ,
,  in the plane, where
in the plane, where 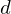 lies in
lies in 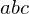 's circumcircle.
's circumcircle.The lifted points
 lie in the same plane as the lifted ellipse of
lie in the same plane as the lifted ellipse of 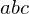 's circumcircle. Since
's circumcircle. Since 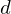 lies inside the circle,
lies inside the circle, lies below the plane of
lies below the plane of 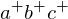 . Thus, the edge
. Thus, the edge  is reflex.
is reflex.By flipping the edge
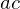 to
to 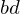 , we replace the reflex edge
, we replace the reflex edge  by the convex edge
by the convex edge  .
.Note that the four points
 form a tetrahedron. Before the flip, our triangulation corresponded to the upward-facing faces of the tetrahedron. After the flip, it corresponded to the downward-facing faces of the tetrahedron.
form a tetrahedron. Before the flip, our triangulation corresponded to the upward-facing faces of the tetrahedron. After the flip, it corresponded to the downward-facing faces of the tetrahedron.Thus, with each flip, we monotonically decrease the height of our triangulation on the paraboloid. Tetrahedral edges which lie on the upward-facing side are never considered again. Thus, the algorithm terminates eventually.
Flashcard info:
Author: janisborn
Main topic: Informatik
Topic: Computergrafik
School / Univ.: RWTH Aachen
City: Aachen
Published: 18.05.2022

