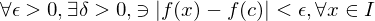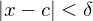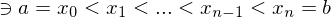Supremum
Suppose  is bounded above. A number
is bounded above. A number 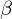 is the supremum of
is the supremum of  if
if 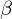 is an upper bound of
is an upper bound of  and any number less the
and any number less the 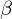 is not an upper bound of
is not an upper bound of  . We write
. We write 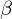 = sup
= sup 
 is bounded above. A number
is bounded above. A number 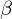 is the supremum of
is the supremum of  if
if 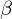 is an upper bound of
is an upper bound of  and any number less the
and any number less the 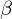 is not an upper bound of
is not an upper bound of  . We write
. We write 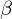 = sup
= sup 
Infimum
Suppose  is bounded below. A number
is bounded below. A number 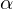 is the infimum of
is the infimum of  if
if 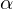 is a lower bound of
is a lower bound of  and any number greater the
and any number greater the 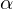 is not a lower bound of
is not a lower bound of  . We write
. We write 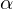 = inf
= inf 
 is bounded below. A number
is bounded below. A number 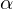 is the infimum of
is the infimum of  if
if 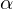 is a lower bound of
is a lower bound of  and any number greater the
and any number greater the 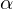 is not a lower bound of
is not a lower bound of  . We write
. We write 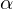 = inf
= inf 
Converges to a number L
A sequence {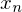 } converges to a number
} converges to a number 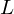 if
if
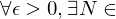 Z
Z 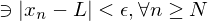 . The number
. The number 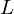 is called the limit of the sequence and the notation
is called the limit of the sequence and the notation 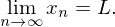
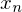 } converges to a number
} converges to a number 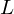 if
if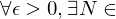 Z
Z 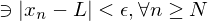 . The number
. The number 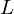 is called the limit of the sequence and the notation
is called the limit of the sequence and the notation 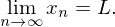
Bounded Below
The set  is bounded below if there is a number
is bounded below if there is a number 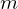 such that
such that 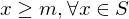 . The number
. The number 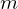 is called a lower bound of
is called a lower bound of  .
.
 is bounded below if there is a number
is bounded below if there is a number 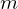 such that
such that 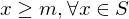 . The number
. The number 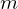 is called a lower bound of
is called a lower bound of  .
.Bounded Above
The set  is bounded above if there is a number
is bounded above if there is a number 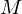 such that
such that 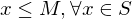 . The number
. The number 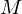 is called an upper bound of
is called an upper bound of  .
.
 is bounded above if there is a number
is bounded above if there is a number 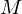 such that
such that 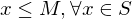 . The number
. The number 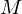 is called an upper bound of
is called an upper bound of  .
.Bounded
The set  is bounded if there is a number
is bounded if there is a number 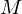 such that
such that 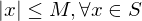 . The number
. The number 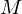 is called a bound for
is called a bound for  .
.
 is bounded if there is a number
is bounded if there is a number 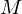 such that
such that 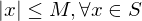 . The number
. The number 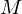 is called a bound for
is called a bound for  .
.Interval
A set  of real numbers is an interval iff
of real numbers is an interval iff  contains at least 2 points and for any two points
contains at least 2 points and for any two points 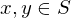 , every real number between
, every real number between 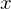 and
and  belong to
belong to  as well.
as well.
 of real numbers is an interval iff
of real numbers is an interval iff  contains at least 2 points and for any two points
contains at least 2 points and for any two points 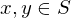 , every real number between
, every real number between 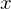 and
and  belong to
belong to  as well.
as well.Finite
A set 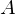 is finite if it is empty or if its elements can be put in a one to one correspondence with the set {1,2,...,n} for some n.
is finite if it is empty or if its elements can be put in a one to one correspondence with the set {1,2,...,n} for some n.
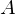 is finite if it is empty or if its elements can be put in a one to one correspondence with the set {1,2,...,n} for some n.
is finite if it is empty or if its elements can be put in a one to one correspondence with the set {1,2,...,n} for some n.Countably Infinite
The set 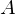 is countably infinite if its elements can be put in a one to one correspondence with the set of positive integers
is countably infinite if its elements can be put in a one to one correspondence with the set of positive integers
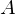 is countably infinite if its elements can be put in a one to one correspondence with the set of positive integers
is countably infinite if its elements can be put in a one to one correspondence with the set of positive integersSubsequence
Let 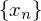 be a squence and let
be a squence and let 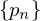 be a strictly increasing sequence of positive integers.
be a strictly increasing sequence of positive integers.
The sequence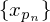 is called a subsequence of
is called a subsequence of 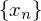
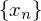 be a squence and let
be a squence and let 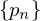 be a strictly increasing sequence of positive integers.
be a strictly increasing sequence of positive integers.The sequence
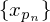 is called a subsequence of
is called a subsequence of 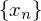
Order
<, on a set  is a relation with the following properties;
is a relation with the following properties;
Trichotomy, if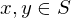 , then only 1 of the following holds;
, then only 1 of the following holds; 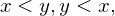 or
or 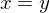
Transitivity,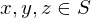 , if
, if 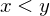 and
and 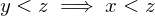
 is a relation with the following properties;
is a relation with the following properties;Trichotomy, if
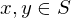 , then only 1 of the following holds;
, then only 1 of the following holds; 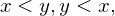 or
or 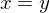
Transitivity,
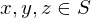 , if
, if 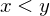 and
and 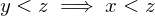
Field
A non empty set, 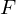 , with
, with 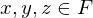 , with 2 operations, + and * w the following properties;
, with 2 operations, + and * w the following properties;
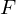 , with
, with 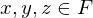 , with 2 operations, + and * w the following properties;
, with 2 operations, + and * w the following properties;| Closure | 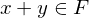 | 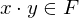 |
| Commutative | 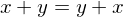 | 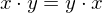 |
| Associative | 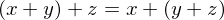 | 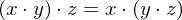 |
| Identity | 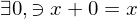 |  |
| Inverse | 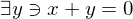 | 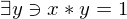 |
| Distributive | 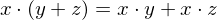 |
Squeeze Theorem for Functions
Let I be an open interval containing point c and suppose 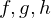 are functions defined on I except pssibly at c.
are functions defined on I except pssibly at c.
Suppose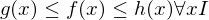 \{c}
\{c}
if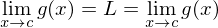 then f has limit at c and
then f has limit at c and 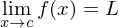
 are functions defined on I except pssibly at c.
are functions defined on I except pssibly at c.Suppose
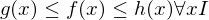 \{c}
\{c}if
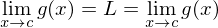 then f has limit at c and
then f has limit at c and 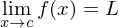
Subsequential Limit
The Subsequential limit of 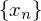 is any real number, x, such that there exists a subsequence of
is any real number, x, such that there exists a subsequence of 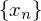 that converges to x
that converges to x
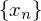 is any real number, x, such that there exists a subsequence of
is any real number, x, such that there exists a subsequence of 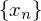 that converges to x
that converges to xDifferentiable at c
Let  be an interval, let
be an interval, let 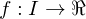 , and let
, and let 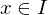 . The function
. The function 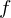 is differentiable at c provided that the limit
is differentiable at c provided that the limit
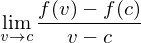
exists. The derivative of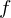 at c is the value of the limit and noted by
at c is the value of the limit and noted by 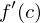
 be an interval, let
be an interval, let 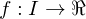 , and let
, and let 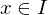 . The function
. The function 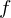 is differentiable at c provided that the limit
is differentiable at c provided that the limit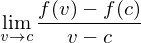
exists. The derivative of
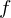 at c is the value of the limit and noted by
at c is the value of the limit and noted by 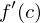
Uniformly continuous
Let  be an interval. A function
be an interval. A function 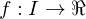 is uniformly continuous on
is uniformly continuous on  if
if 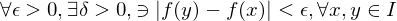 that satisfy
that satisfy 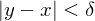 .
.
 be an interval. A function
be an interval. A function 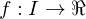 is uniformly continuous on
is uniformly continuous on  if
if 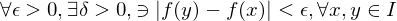 that satisfy
that satisfy 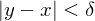 .
.Chain Rule
Let  be an interval,
be an interval, 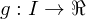 ,
,
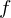 is defined on
is defined on 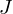 that contains
that contains 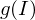
if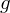 is differentiable on
is differentiable on  , and
, and 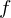 is differentiable on
is differentiable on 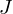 then
then 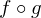 is differentiable on
is differentiable on  and
and
 be an interval,
be an interval, 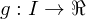 ,
,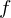 is defined on
is defined on 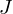 that contains
that contains 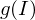
if
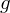 is differentiable on
is differentiable on  , and
, and 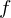 is differentiable on
is differentiable on 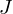 then
then 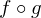 is differentiable on
is differentiable on  and
and
Intermediate Value Property
A function 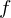 defined on an interval
defined on an interval  has the intermediate value property on
has the intermediate value property on  if it satisfies the following condition: if
if it satisfies the following condition: if 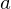 and
and 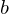 are distinct points in
are distinct points in  and
and 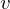 is any number between
is any number between 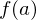 and
and 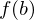 , then there exists a point
, then there exists a point  between
between 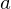 and
and 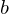 such that
such that 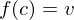
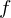 defined on an interval
defined on an interval  has the intermediate value property on
has the intermediate value property on  if it satisfies the following condition: if
if it satisfies the following condition: if 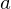 and
and 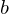 are distinct points in
are distinct points in  and
and 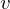 is any number between
is any number between 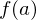 and
and 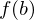 , then there exists a point
, then there exists a point  between
between 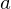 and
and 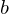 such that
such that 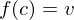
Limit Superior
if 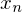 is bounded above then the limit superior is defined by
is bounded above then the limit superior is defined by 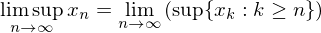
if not bounded above then the limit superior=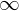
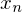 is bounded above then the limit superior is defined by
is bounded above then the limit superior is defined by 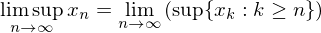
if not bounded above then the limit superior=
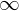
Limit Inferior
if 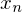 is bounded below then the limit inferior is defined by
is bounded below then the limit inferior is defined by 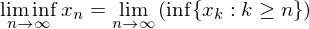
if not bounded below then the limit inferior = -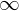
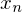 is bounded below then the limit inferior is defined by
is bounded below then the limit inferior is defined by 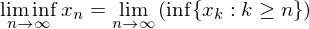
if not bounded below then the limit inferior = -
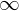
Right Hand Limit
 is an open interval containing
is an open interval containing  or
or  is at endpoint.
is at endpoint.  is a function defined on
is a function defined on  except maybe at
except maybe at 
if
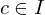 or if
or if  is left endpoint, then
is left endpoint, then 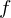 has right hand limit L at c if
has right hand limit L at c if 
Left Hand Limit
 is an open interval containing
is an open interval containing  or
or  is at endpoint.
is at endpoint. 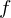 is a function defined on
is a function defined on  except maybe at
except maybe at 
if
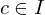 or if
or if  is right endpoint, then
is right endpoint, then 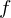 has left hand limit L at c if
has left hand limit L at c if 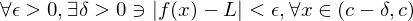
Jump Discontinuity
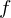 has jump discontinuity at
has jump discontinuity at  if the one sided limits exist but are not equal
if the one sided limits exist but are not equalRemovable Discontinuity
at c if 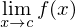 exists, but
exists, but 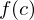 is either not defined or has a different value from the limit as x approaches c
is either not defined or has a different value from the limit as x approaches c
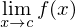 exists, but
exists, but 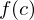 is either not defined or has a different value from the limit as x approaches c
is either not defined or has a different value from the limit as x approaches cTagged Partition
A tagged partition 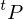 of an interval
of an interval 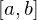 consists of a partition
consists of a partition
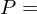 {
{ 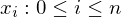 } of
} of 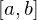 along with the set
along with the set
{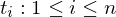 } of points, known as tags, that satisfy
} of points, known as tags, that satisfy 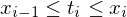 for
for 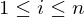 .
.
We will express a tagged partition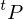 of
of 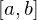 by
by
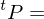 {
{ 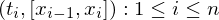 }
}
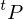 of an interval
of an interval 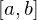 consists of a partition
consists of a partition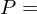 {
{ 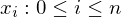 } of
} of 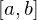 along with the set
along with the set{
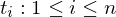 } of points, known as tags, that satisfy
} of points, known as tags, that satisfy 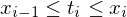 for
for 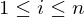 .
.We will express a tagged partition
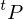 of
of 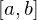 by
by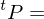 {
{ 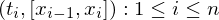 }
}Norm of Partition, ||P||
The Norm of the partition P, ||P|| = max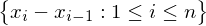
If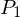 and
and 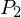 are partitions of
are partitions of 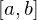 and
and  is a refinement of
is a refinement of 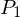
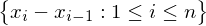
If
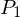 and
and 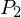 are partitions of
are partitions of 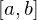 and
and  is a refinement of
is a refinement of 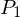
Riemann Sum
Let 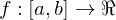 and let
and let 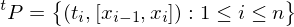 be a tagged partition of
be a tagged partition of 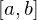 . The Riemann sum
. The Riemann sum 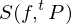 of
of 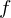 associated with
associated with 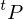 is defined by:
is defined by:
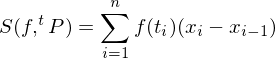
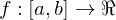 and let
and let 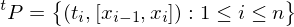 be a tagged partition of
be a tagged partition of 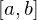 . The Riemann sum
. The Riemann sum 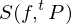 of
of 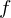 associated with
associated with 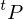 is defined by:
is defined by: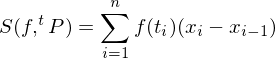
Riemann Integrable
A function 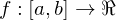 is Riemann integrable on
is Riemann integrable on 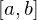 if there exists a number
if there exists a number 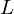 with the following property: for each
with the following property: for each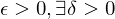 , such that
, such that 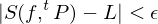 , for all tagged partitions
, for all tagged partitions 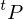 of
of 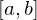 that satisfy
that satisfy 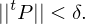
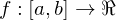 is Riemann integrable on
is Riemann integrable on 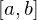 if there exists a number
if there exists a number 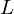 with the following property: for each
with the following property: for each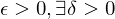 , such that
, such that 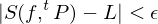 , for all tagged partitions
, for all tagged partitions 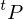 of
of 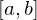 that satisfy
that satisfy 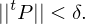
Riemann integral
The number L is called the Riemann integral of 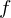 on
on 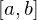 and is denoted by the symbol
and is denoted by the symbol 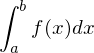 , or simply
, or simply 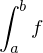 .
.
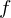 on
on 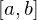 and is denoted by the symbol
and is denoted by the symbol 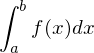 , or simply
, or simply 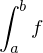 .
.Kartensatzinfo:
Autor: Squiggleart
Oberthema: Mathematics
Thema: Advanced Calculus
Schule / Uni: West Chester University
Veröffentlicht: 25.05.2011
Schlagwörter Karten:
Alle Karten (51)
keine Schlagwörter



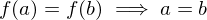
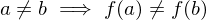
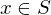 such that
such that 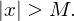
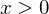 and
and 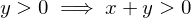
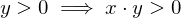
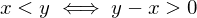
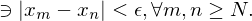
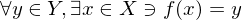
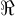 that is bounded above has a supremum
that is bounded above has a supremum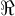 is an interval if it has the properties that if
is an interval if it has the properties that if 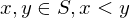 , and
, and 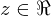 , then if
, then if 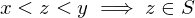
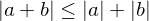
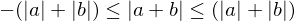
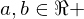 , and
, and 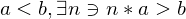
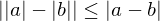

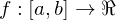 is continuous on
is continuous on 
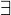 c,d
c,d 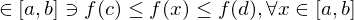
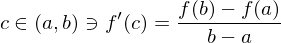
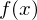 at c
at c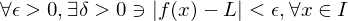 that satisfy
that satisfy 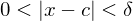
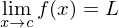
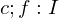 {
{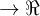
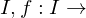 .
.