This flashcard is just one of a free flashcard set. See all flashcards!
98
Name and explain three mesh data structures for geometry processing!
Face Based
Store, for every face:
Problem: For arbitrary meshes, entries can be of different size (because of varying face valence)
Edge Based
Store, for every edge:
Advantage: Constant storage per entry
Problem: Start and end point are chosen arbitrarily. Traversal in both directions requires case distinctions.
Halfedge Based
Store, for every halfedge:
Advantage: Constant storage per entry, no directional ambiguity, can only represent manifold meshes
Enumerating 1-Ring Neighborhood
1. pick one outgoing halfedge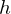 from center vertex
from center vertex
2. do something with the current target vertex
3. go to the opposite halfedge
4. go to the next halfedge
5. if the current halfedge is not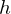 , go to 2
, go to 2
Store, for every face:
- pointers to all face vertices
- pointers to all adjacent faces
Problem: For arbitrary meshes, entries can be of different size (because of varying face valence)
Edge Based
Store, for every edge:
- 2 pointers to the edge endpoint vertices
- 2 pointers to the incident faces
- 4 pointers to adjacent edges (on each side, one in cw / ccw direction)
Advantage: Constant storage per entry
Problem: Start and end point are chosen arbitrarily. Traversal in both directions requires case distinctions.
Halfedge Based
Store, for every halfedge:
- pointer to target vertex
- pointer to incident face (to the left)
- pointer to next halfedge (leftmost outgoing halfedge from target vertex)
- pointer to opposite halfedge (not explicitly stored: store list of halfedge pairs. obtain pointer to opposite halfedge by flipping last bit of index)
- (sometime: previous halfedge)
Advantage: Constant storage per entry, no directional ambiguity, can only represent manifold meshes
Enumerating 1-Ring Neighborhood
1. pick one outgoing halfedge
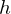 from center vertex
from center vertex2. do something with the current target vertex
3. go to the opposite halfedge
4. go to the next halfedge
5. if the current halfedge is not
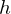 , go to 2
, go to 2Flashcard info:
Author: janisborn
Main topic: Informatik
Topic: Computergrafik
School / Univ.: RWTH Aachen
City: Aachen
Published: 18.05.2022

